Today I am going to give you a tip for getting started with Extension Building for Business Central.
As AL have newly introduced so it is going to take time to learn and be comfortable with programming using AL codes.
Best way of learning anything is learning by examples. What if we first learn what will be equivalent to actions we perform in Navision designer.
So to demonstrate this I will start with creating a small customization directly in Navision then convert it to Extension.
Are you ready? Let’s start with this exciting journey of 1-2-3 step.
Step 1.
Saving my Base Line Object (Prior to performing any Modification).
In this example I am going to Modify Table – Item & Page Item Card.
Let’s export this two object as FOB, Later we will require this to revert our customization.
Also export this two objects as txt. This we will require in our Extension building process. But need to follow instructions explained in below step, else this file will be rejected by the tool when we try to convert to AL. Follow the process of exporting text file explained after completing the Customizations in Step 3.
Step 2.
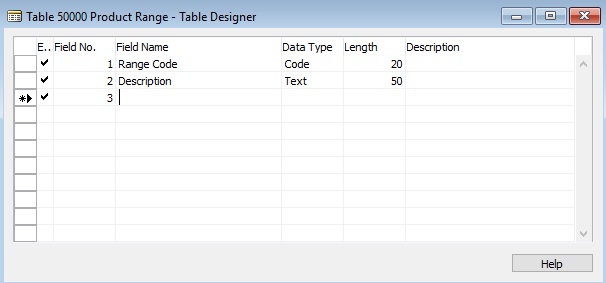
I will create one Table 50000 – Product Range as below:
Next I will create one List Page on above Table, Page 50000 – Product Range as below:
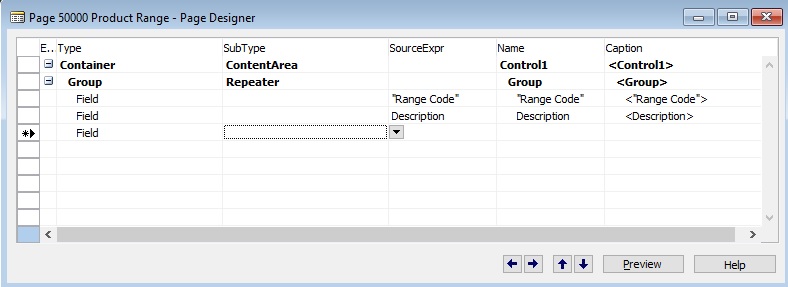
Also will Add Table Property as below to enable Lookup & DrillDown

Save your objects.
Now I will add one field to Table Item & Page Item Card as below:
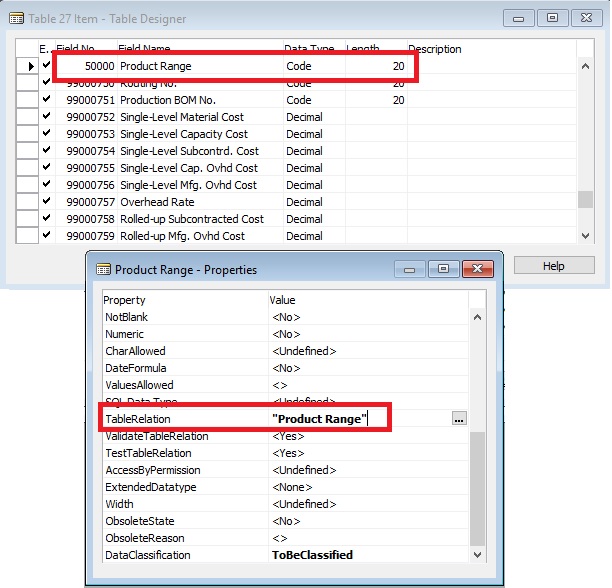
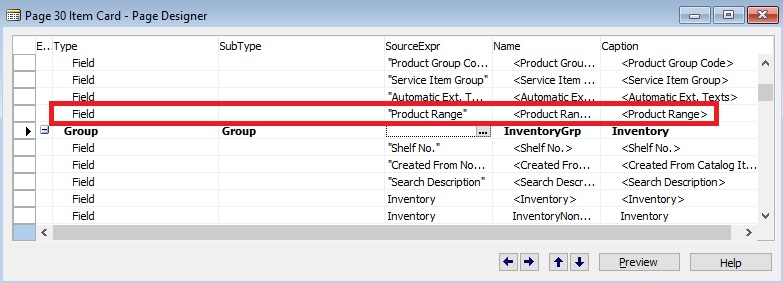
Now I am done with my all customization and saved my modified & New Objects.
Step 3.
Now we will export these objects All New & Modified into Text File.
But we will not do it from Object designer rather will do it from command prompt.
Preparing for AL Conversion.
Run Command Prompt as Administrator.
Change to RTC folder.
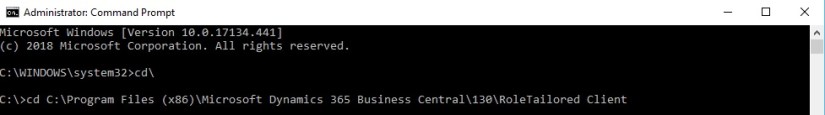
Check your folder where you have installed, default location is as one I am using.
You can export all objects in one single file or one file per object. I am exporting one object per file, you can explore command parameter to use accordingly.
I will be using below commands.
First we will create 4 Folders namely Original, Modified, Delta & Result
Note: Make sure ExportToNewSyntax with command parameter is used else txt2al (which we will use below) will reject your files, it is mandatory.
Below command is to export Original objects before modification: (Save in Original Folder)
1. finsql.exe Command=ExportToNewSyntax, File=G:\RND\Txt2ALTest\exportedBaselineObjectsT27.txt, Database=”Demo Database NAV (13-0)”, ServerName=”KSD-DESKTOP” ,Filter=Type=table;ID=27
2. finsql.exe Command=ExportToNewSyntax, File=G:\RND\Txt2ALTest\exportedBaselineObjectsP30.txt, Database=”Demo Database NAV (13-0)”, ServerName=”KSD-DESKTOP” ,Filter=Type=page;ID=30
Below command is for New Objects: (Save in Modified Folder)
3. finsql.exe Command=ExportToNewSyntax, File=G:\RND\Txt2ALTest\exportedNewObjectsT50000.txt, Database=”Demo Database NAV (13-0)”, ServerName=”KSD-DESKTOP” ,Filter=Type=table;ID=50000
4. finsql.exe Command=ExportToNewSyntax, File=G:\RND\Txt2ALTest\exportedNewObjectsP50000.txt, Database=”Demo Database NAV (13-0)”, ServerName=”KSD-DESKTOP” ,Filter=Type=page;ID=50000
Below command is for Modified Objects: (Save in Modified Folder)
5. finsql.exe Command=ExportToNewSyntax, File=G:\RND\Txt2ALTest\exportedModifiedObjectsT27.txt, Database=”Demo Database NAV (13-0)”, ServerName=”KSD-DESKTOP” ,Filter=Type=table;ID=27
6. finsql.exe Command=ExportToNewSyntax, File=G:\RND\Txt2ALTest\exportedModifiedObjectsP30.txt, Database=”Demo Database NAV (13-0)”, ServerName=”KSD-DESKTOP” ,Filter=Type=page;ID=30
Our Next step will be to create DELTA files.
Open Business Central Administration Shell
Import your Microsoft.Dynamics.Nav.Model.Tools Module using below syntax
import-module “C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central\130\RoleTailored Client\Microsoft.Dynamics.Nav.Model.Tools.psd1” -force –verb
Execute below Shell Command:
Compare-NAVApplicationObject -OriginalPath G:\RND\Txt2ALTest\Original\*.txt -ModifiedPath G:\RND\Txt2ALTest\Modified\*.txt -DeltaPath G:\RND\Txt2ALTest\DELTA\ -ExportToNewSyntax
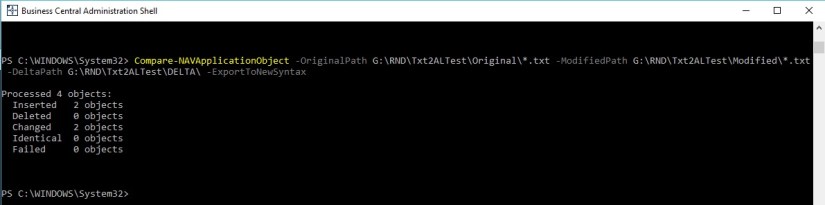
After this process we will get our Delta files in Delta Folder, this will be input to our next command/tool.
Next we will convert Delta File to AL files.
On Command prompt used above run below command: (This is not Shell Window please make sure)
txt2al –source G:\RND\Txt2ALTest\DELTA\ –target G:\RND\Txt2ALTest\RESULT\

Here we will get our *.al files. Which will be used for creating extensions.
Step 4.
Perform clean up to the database.
- Import the FOB exported in Step one to restore your original Table 27 & Page 30.
- Delete New Created Objects.
Now our database in in original state as before performing customization.
Fresh and Clean Business Central Database without any customizations.
Step 5.
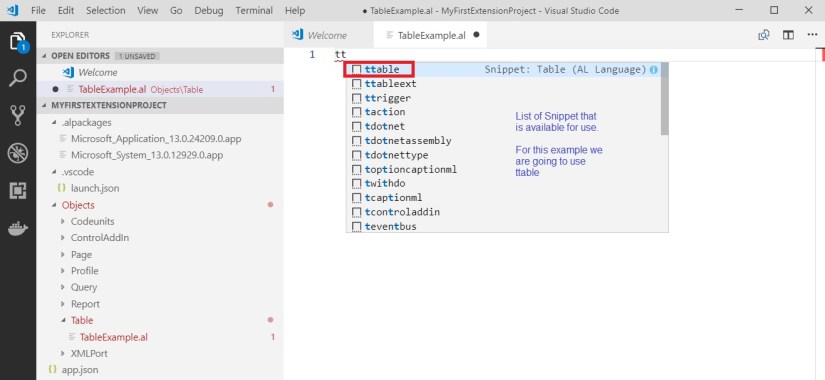
In this step we will create extension in VS Code using above obtained *.al file.
Open VS Code and Press <Ctrl>+<Shift>+<P> and select AL:Go! to create a project Folder
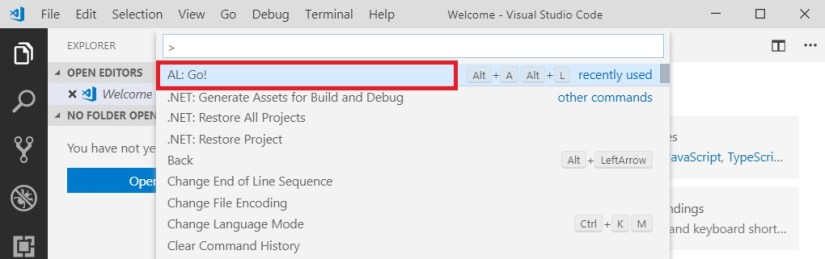
Enter your Project Folder and press enter

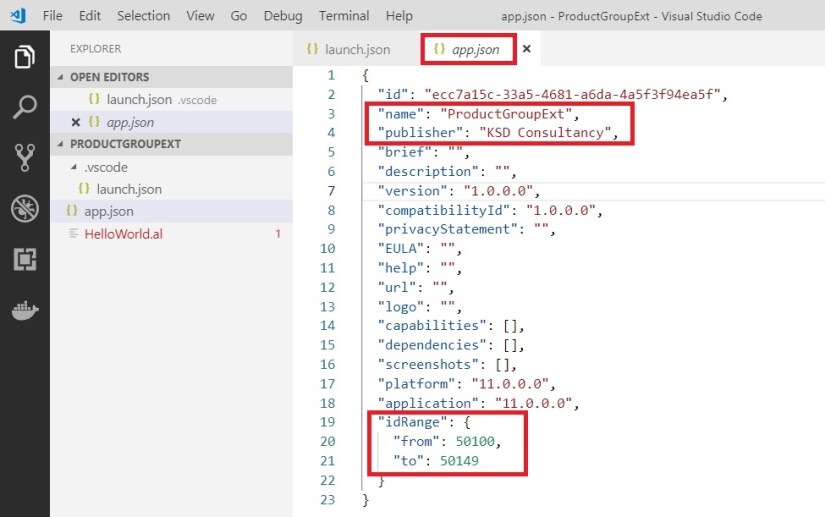
Update your app.json file as below:
Add Name & Publisher, also check available idRange all objects in this project must be in this Range.
Update your launch.json file with your server & authentication details accordingly:
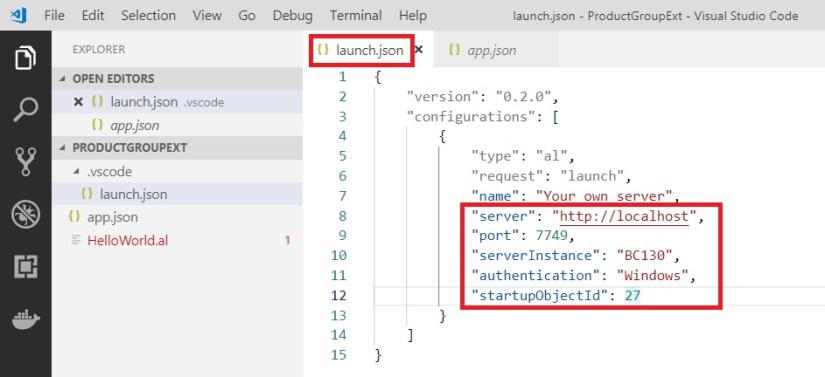
Remove the HelloWorld.al file created by default by right click and select delete.
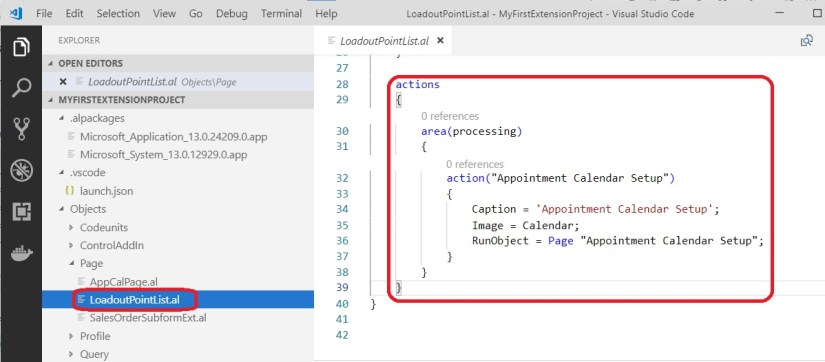
Now add your created *.al files

You can drag and Drop to your Project Folder.
Now you will get errors, to resolve it we need to download our Symbols from Navision.
To download press <Ctrl>+<Shift>+<P> to open command Pallet and select Al: Download Symbols
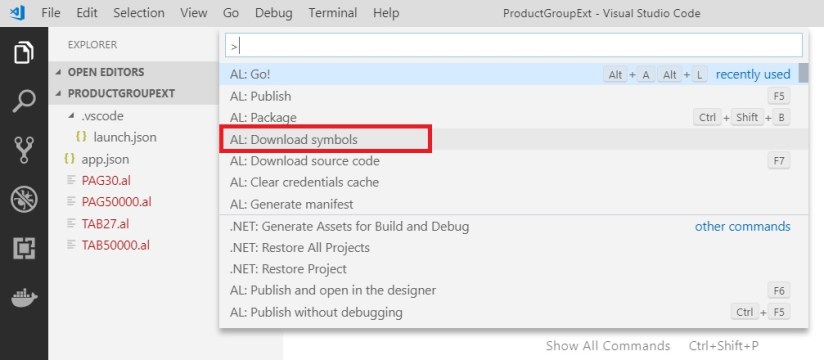
If your server settings in launch.jason is correct your Symbols will get downloaded.

Now let resolve any others errors that may have in your *.al Files.
First I will rename my all Files to meaningful name so that in future it is easy to manage.
To do so, right click the File and select Rename, in my case I have renamed as below:

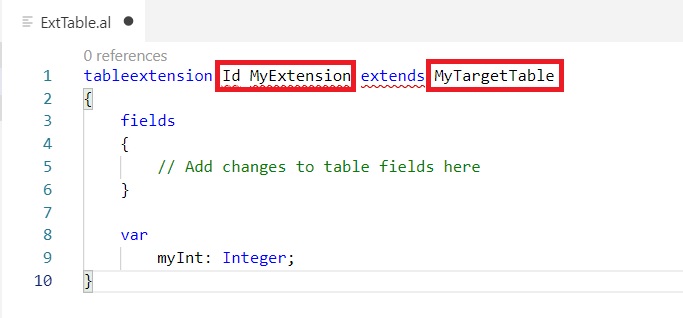
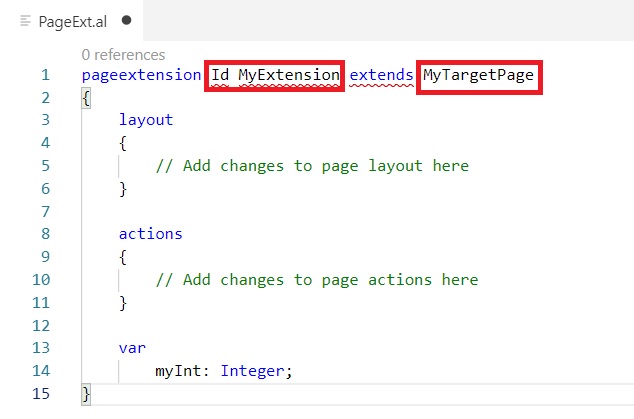
Now we will open each file and perform required action to resolve the errors as below.
After changes don’t forget to save your files.


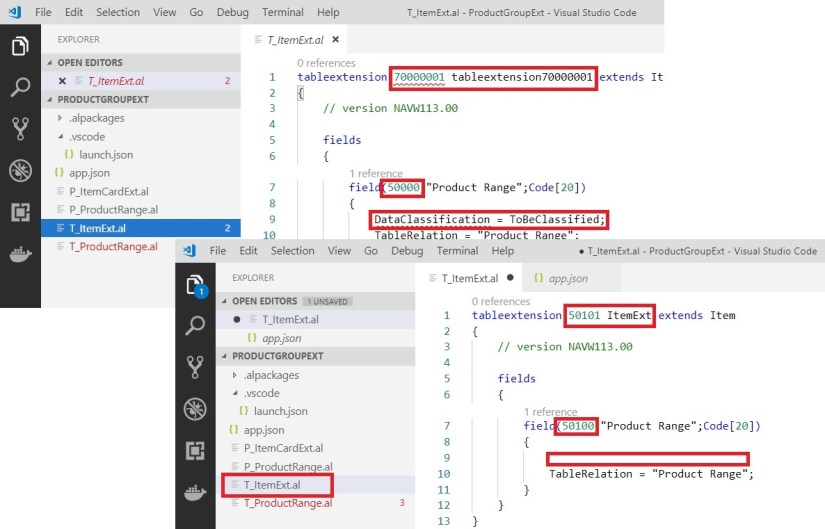
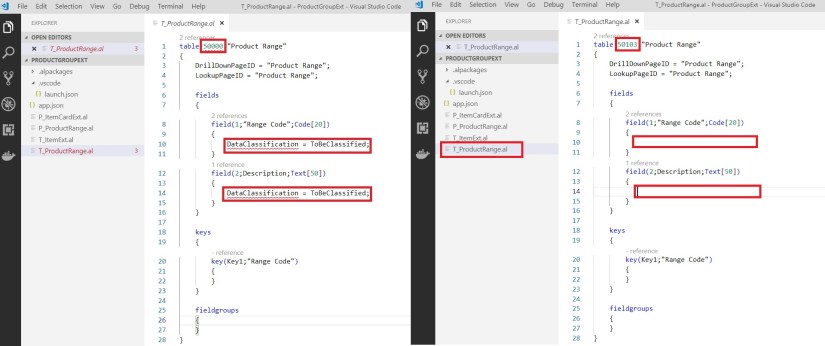
Ensure Object ID you use is within the range of id provided in app.json file. ID is not used in database or any other extensions. Else when you deploy the extension it will give errors, also make sure you give unique object names too.
DataClassification property is not available in Al so we removed it.
Now my all objects are error free, and ready to be packaged.
Step 6.
Now we will Deploy & Test our Extension.
To create a package press <Ctrl>+<Shift>+<P> to open command pallet.
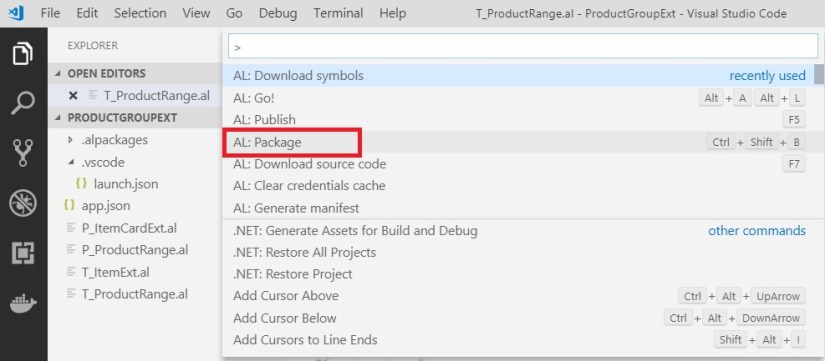
You can choose AL:Publish also it will create package and Publish to the server.
Next you choose AL:Publish to deploy your Extension to the Business Central.
You can verify your Extension from Extension Management Page from Navision Client
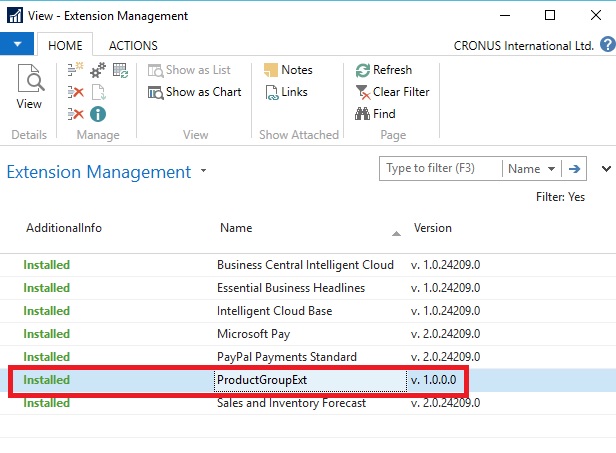
Double click on your extension record to see details:

Now let’s see in action our extension.
Open Item Card.

Congrats, your First Extension is ready to use.
There is lots of many thing to explain, but in single post everything is not possible. I will come up with basic things and creating Extensions from scratch in some other posts.
It was just a quick idea, as everyone is looking option for upgrade so this information may be handy to plan their next move.
We will learn basics of AL and other fundamental things in our upcoming posts.
Before I close this post will like to share few more details to complete this post.
If you check your Navision you will not find any object or additional fields we added in our extension, then where is my data stored?
Let’s have look in SQL.
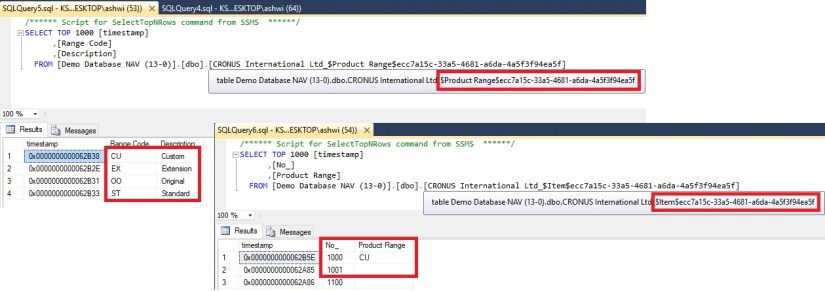
Item Extension & Product Group table is created with your app id of the extension.
We will discuss in more details about other things in details in our next upcoming posts.
Till then keep learning, and stay safe, take care.
28.629409
77.432905

















































You must be logged in to post a comment.