Administrators can record new permission sets in Microsoft Dynamics NAV 2016.
Recording permissions is based on the code coverage functionality.
You can access the various windows and activities in the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Windows client or the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Web client that you want users with this permission set to access.
You must carry out the tasks that you want to record permissions for. Then, you can apply the new permission set to a group of users.
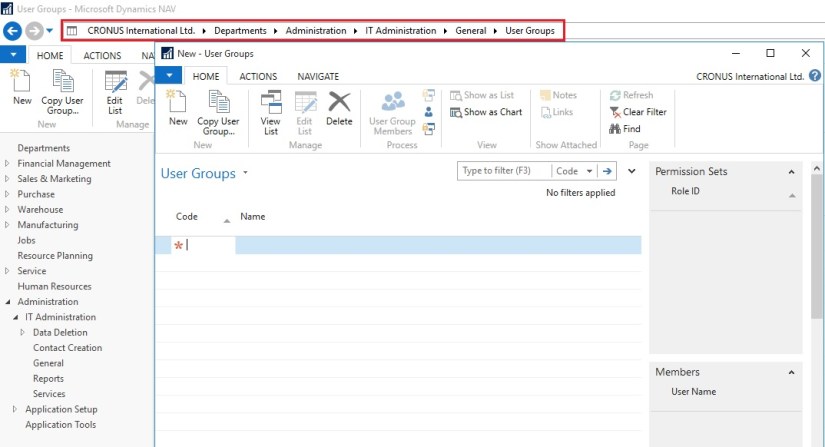
A user group is a combination of roles and users. If you want to change permissions for the user group, the changes are automatically applied to the users who are members of the group.
To help you manage permissions in Microsoft Dynamics NAV for your company, you can set up one or more user groups, add permissions sets to the groups, and then add users to the groups. You can add more than one permission set to a user group.
In the User Groups window, you can set up user groups, add and remove permissions, and you can apply changes to all or specific user groups.




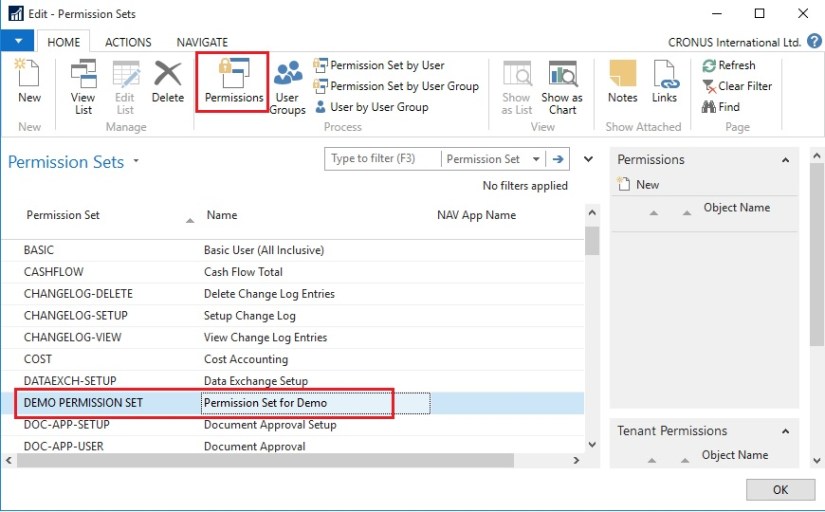
If the default permission sets that are provided with Microsoft Dynamics NAV are not sufficient or not appropriate for your organization, then you can create new permission sets. If the individual object permissions that define a permission set are not adequate, then you can modify a permission set.
You can create a permission set manually, or you can record permissions by navigating in the application.


This starts a recording process that is based on the code coverage functionality in Microsoft Dynamics NAV. You can now access the various windows and activities in the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Windows client or the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Web client that you want users with this permission set to access. You must carry out the tasks that you want to record permissions for.
When you want to finish the recording, return to the Permissions window, and then, on the Actions tab, choose Stop.
Choose Yes to add the recorded permissions to the new permission set, or choose No to cancel.
If you choose Yes, the objects that you accessed are added to the window. In Microsoft Dynamics NAV 2016, only the objects are recorded, so you must specify if users must be able to insert, modify, or delete records in the recorded tables.
28.620561
77.437322




























You must be logged in to post a comment.