Recall from my previous post Add a relationship using Diagram View in Power Pivot
Which I have left with below note. I will be continuing from where I left my previous post.
It’s nice when the data in your Data Model has all the fields necessary to create relationships, and mash up data to visualize in Power View or PivotTables. But tables aren’t always so cooperative, so in today’s post will describe how to create a new column, using DAX that can be used to create a relationship between tables.
Open the Olympics Excel sheet which we used in our previous post.

Delete the column EditionID from sheet Medals & Hosts Table/Sheet.
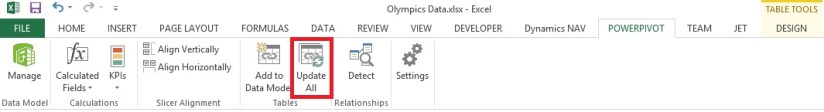
After deleting the Column EditionID from Table/Sheet Select Update All in Ribbon from PowerPivot Tab. This will update the column in Data Model.
Since we are going to learn creating relationship on calculated fields.
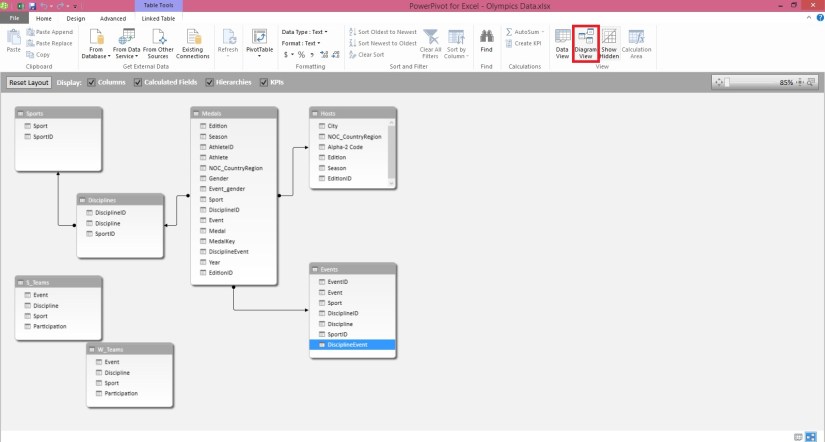
In Hosts, we can create a unique calculated column by combining the Edition field (the year of the Olympics event) and the Season field (Summer or Winter). In the Medals table there is also an Edition field and a Season field, so if we create a calculated column in each of those tables that combines the Edition and Season fields, we can establish a relationship between Hosts and Medals. The following screen shows the Hosts table, with its Edition and Season fields selected
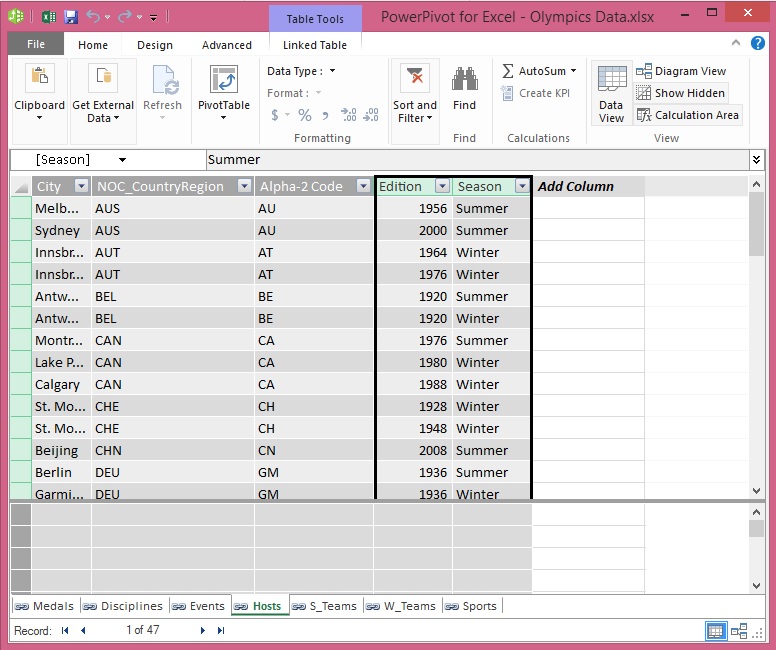
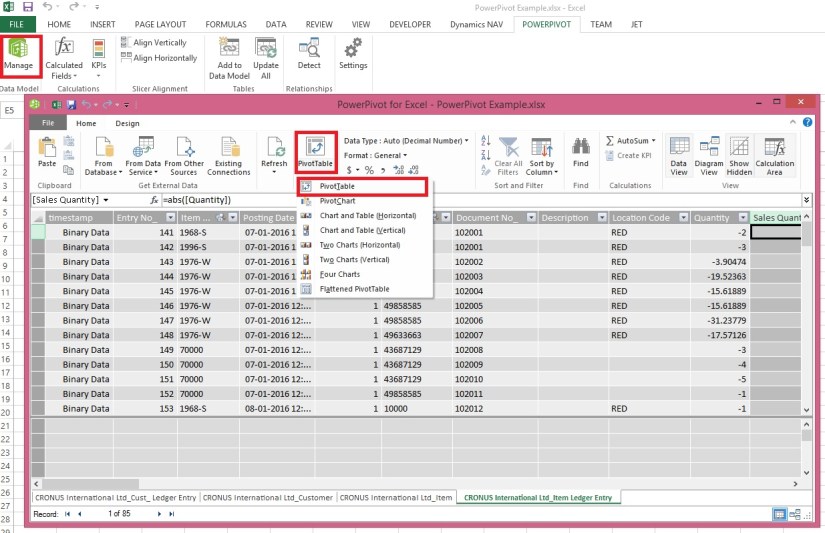
Select the Hosts table in Power Pivot. Adjacent to the existing columns is an empty column titled Add Column. Power Pivot provides that column as a placeholder. There are many ways to add a new column to a table in Power Pivot, one of which is to simply select the empty column that has the title Add Column.
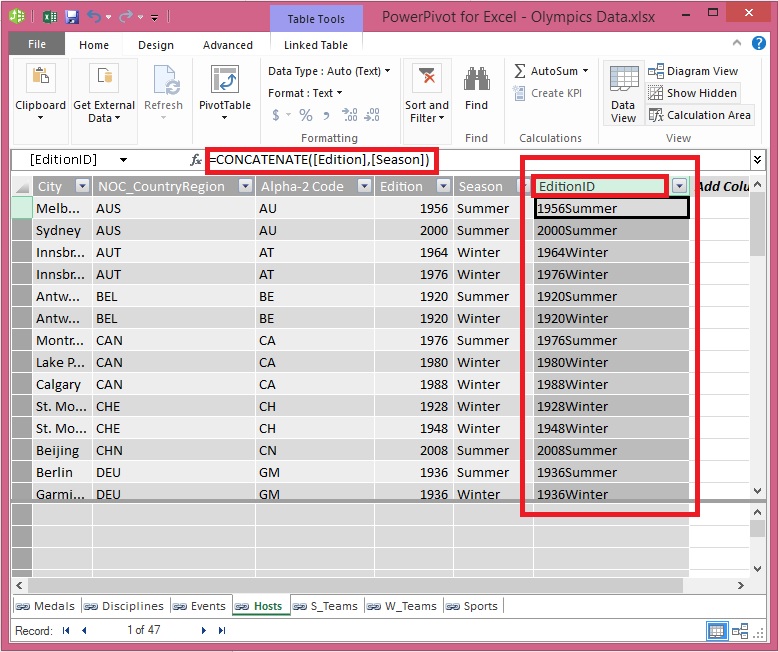
In the formula bar, type the following DAX formula. The CONCATENATE function combines two or more fields into one. As you type, AutoComplete helps you type the fully qualified names of columns and tables, and lists the functions that are available. Use tab to select AutoComplete suggestions. You can also just click the column while typing your formula, and Power Pivot inserts the column name into your formula.
=CONCATENATE([Edition],[Season])
When you finish building the formula, press Enter to accept it.
Values are populated for all the rows in the calculated column. If you scroll down through the table, you see that each row is unique – so we’ve successfully created a field that uniquely identifies each row in the Hosts table. Such fields are called a primary key.
Let’s rename the calculated column to EditionID. You can rename any column by double-clicking it, or by right-clicking the column and choosing Rename Column. When completed, the Hosts table in Power Pivot looks like the following screen.
Next let’s create a calculated column in Medals that matches the format of the EditionID column we created in Hosts, so we can create a relationship between them.
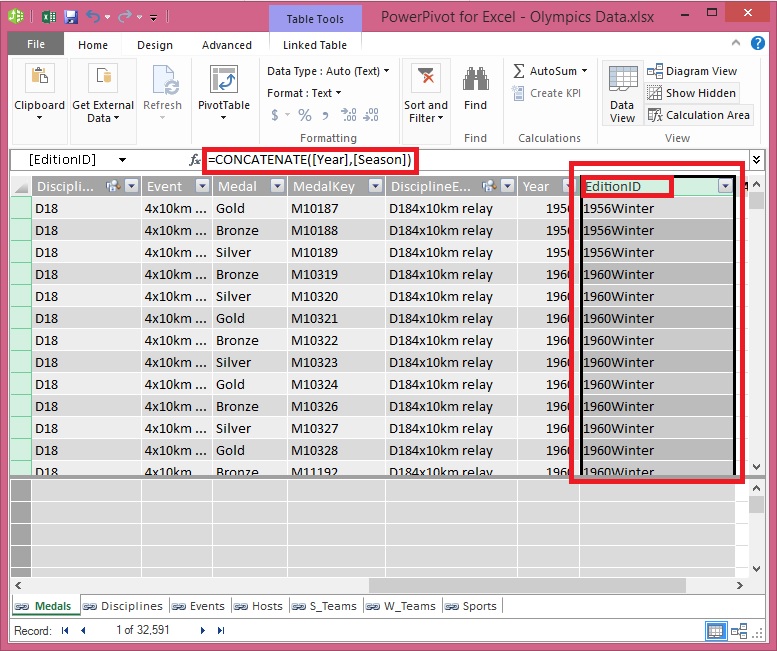
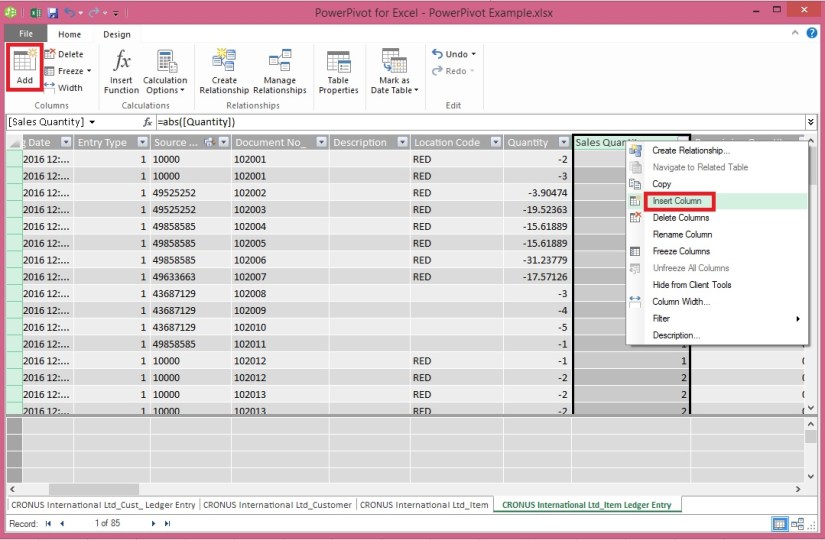
When you created a new column, Power Pivot added another placeholder column called Add Column. Next we want to create the EditionID calculated column, so select Add Column. In the formula bar, type the following DAX formula and press Enter.
=CONCATENATE([Year],[Season])
Rename the column by double-clicking CalculatedColumn1 and typing EditionID.
Next let’s use the calculated columns we created to establish a relationship between Hosts and Medals.
In the Power Pivot window, select Home > View > Diagram View from the ribbon.
Drag the EditionID column in Medals to the EditionID column in Hosts. Power Pivot creates a relationship between the tables based on the EditionID column, and draws a line between the two columns, indicating the relationship.

Now you can see the relationship between Host & Medal table is established on calculated field EditionID in both the tables.
Stay tuned for more details on this topic. I will come up with next step in this series in my upcoming post.
Till then keep learning & practicing.























You must be logged in to post a comment.