Continuing from my earlier post Upgrading the Application Code in Microsoft Dynamics NAV 2016
At end of previous post we have imported the objects and compiled also resolved any conflicts and compilation error. In the same process we have got the list of objects which were having destructive table schema, means the objects which will be having the changes due to which we could lose some data. Scan the objects and if we wish to save those data then we will be requiring Data Upgrade codeunits to handle any such situation.
How to create you can refer to my earlier post Data Upgrade – in Navision 2015 this it still valid for 2016.
Now we have all the upgraded application objects and Data Upgrade codeunits if any required for the upgrade. So we are good to go with Upgrading Data for Old database.
We will follow below steps to continue, make sure you have followed the process for preparation/ converting of database as discussed in my earlier post Upgrade in Microsoft Dynamics NAV 2016
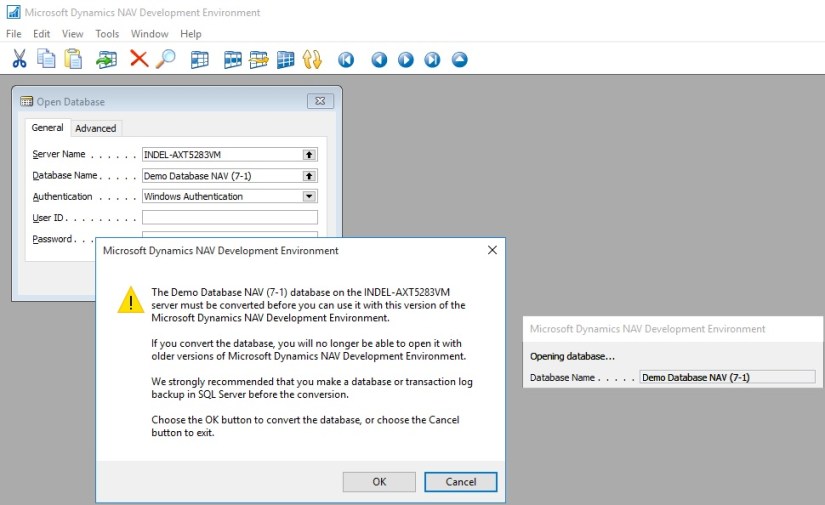
Import the application objects to the converted database
In the development environment, import all the application objects that you extracted in previous step as in my earlier post discussed above in the Microsoft Dynamics NAV 2016 database. This includes the FOB file that contains all the Microsoft Dynamics NAV 2016 objects from the application code upgrade and upgrade toolkit objects if any.
When you import the FOB file, if you experience metadata conflicts, use the Import Worksheet to handle these conflicts.
Finally, on the dialog box for selecting the schema synchronization, set the Synchronize Schema option to Later.

If the upgrade toolkit objects are stored in a separate FOB file, then import the upgrade toolkit FOB file after the application objects are imported.
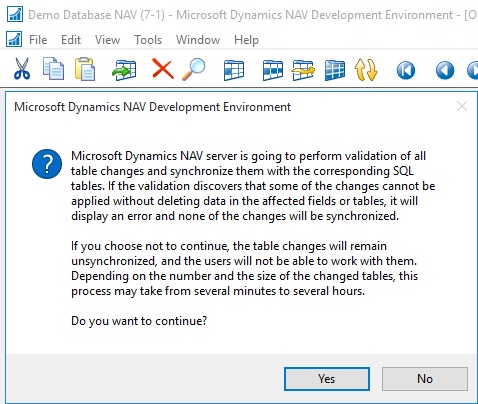
Run the schema synchronization to synchronize the new tables
To publish the data schema changes of the newly imported tables to the SQL tables, run the Sync. Schema For All Tables – With Validation option from the development environment.

If you are confident that any loss of data you are ok with same you can choose Force option which will drop the data for deleted fields, else use Upgrade Codeunit prepared for same as discussed above.
Or alternatively run the Sync-NavTenant cmdlet from the Microsoft Dynamics NAV 2016 Administration Shell.
Sync-NAVTenant –ServerInstance UpgradedDBfrom2013R2 (My Server Instance Name)
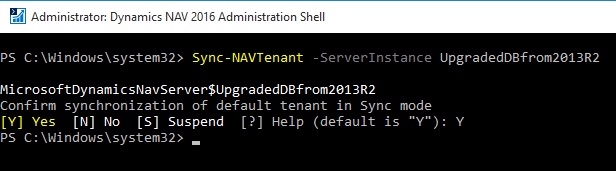
Note this command runs in Administration Shell not in Development Shell as we used in our previous post.
Run the data upgrade process
A data upgrade runs the upgrade toolkit objects, such as upgrade codeunits and upgrade tables, to migrate business data from the old table structure to the new table structure. You can start the data upgrade from the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Development Environment.
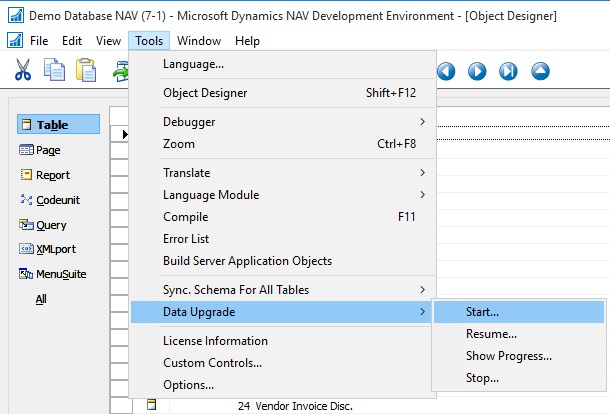

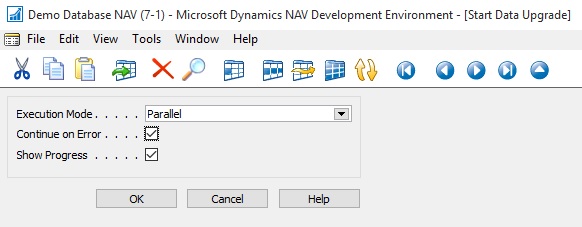

Ooops………….
Or Alternatively Microsoft Dynamics NAV 2016 Administration Shell.
In the last phase of data upgrade, all companies will be initialized by running codeunit 2 Company Initialization. This is done automatically.
If you want to skip company initialization, then use the Start- NavDataUpgrade cmdlet and set the SkipCompanyIntitialization parameter.
Syntax:
Start-NAVDataUpgrade [-ServerInstance] <String> [[-Tenant] <TenantId> ] [[-FunctionExecutionMode] <FunctionExecutionModeValue> ] [[-ContinueOnError]] [-Force] [-Confirm] [-WhatIf] [ <CommonParameters>]
Parameters
-ContinueOnError
Specifies whether the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server instance continues to execute other upgrade functions when an error occurs while executing an upgrade function.
If you do not set this parameter, then when an error occurs, the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server instance will suspend the data upgrade process. It will cancel the execution of upgrade functions currently in progress and roll back any changes that were applied. Completed functions will not be rolled back.
The process remains in suspended state until you take one of the following actions:
– Fix the problems in the upgrade functions that failed, and then resume the process by using the Resume-NAVDataUpgrade cmdlet. You should not add new upgrade functions at this time because they will be ignored when you resume the process.
– Stop the data upgrade process by using the Stop-NAVDataUpgrade cmdlet. Stopping the process will not roll back changes made by upgrade functions that have already been executed.
If you set this parameter, then when an error occurs, the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server instance will continue executing other upgrade functions. At the end of the process, you can use the Get-NAVDataUpgrade cmdlet to see the list of failed upgrade functions. Changes that were applied by completed functions will not be rolled back.
When upgrading a large database, you should increase the SQL Command Timeout setting for the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server instance that connects to the database to avoid timeouts during schema synchronization. The default setting is 30 minutes
-ServerInstance<String>
Specifies the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server instance that the application database and the tenant database are mounted against, such as DynamicsNAV90.
You must include the name within single quotation marks.
-Tenant<TenantId>
Specifies the ID of the tenant that you want to synchronize with the application, such as Tenant1.
This parameter is required unless the specified service instance is not configured to run multiple tenants.
-Force
Forces the command to run without asking for user confirmation.
-FunctionExecutionMode<FunctionExecutionModeValue>
Specifies whether the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server instance executes upgrade functions in series or parallel.
-Confirm
Prompts you for confirmation before running the cmdlet.
-WhatIf
Shows what would happen if the cmdlet runs. The cmdlet is not run.
Few Examples of Usage:
[1] PS C:\> Start-NAVDataUpgrade -ServerInstance DynamicsNAV90 –Force
[2] PS C:\> Start-NAVDataUpgrade -ServerInstance DynamicsNAV90 -ContinueOnError –Force
[3] PS C:\> Start-NAVDataUpgrade -ServerInstance DynamicsNAV90 -FunctionExecutionMode Serial –Force

Start-NAVDataUpgrade -ServerInstance UpgradedDBfrom2013R2 –Force
Ooops………….
Now what to do?
To learn how to Create Data Upgrade Codeunits you can see my earlier posts:
Data Upgrade Codeunit in Navision 2015 – Part -1
Data Upgrade Codeunit in Navision 2015 – Part -2
These posts are still valid for 2016, you can follow to get you task done at this step resolution to above error.
To resolve above issue I have followed the instruction as suggested in error message, but in real scenario you will definitely will be having such codeunits. Since I have taken the 2013-R2 Std. Database I am having this issue. I have created on Upgrade codeunit with an empty upgrade function as below:
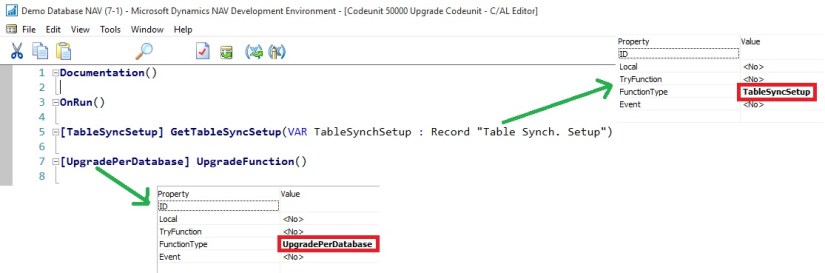
Let us run the above process again.
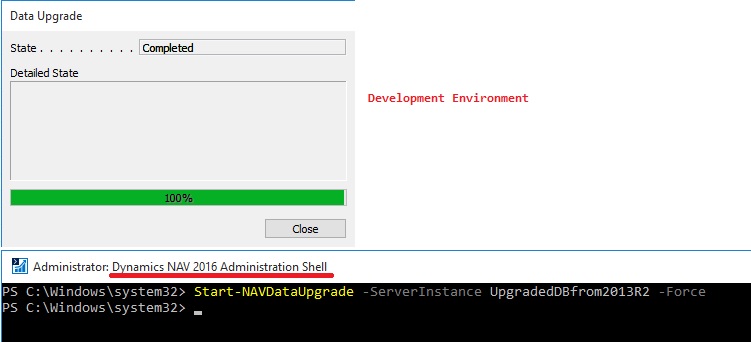
This time I was able to complete the process successfully.
Delete the upgrade objects
At this point, you have upgraded the database to Microsoft Dynamics NAV 2016. Now, you can delete the upgrade codeunits and upgrade table objects that you imported in above step.
When you delete tables, on the Delete dialog box, set the Synchronize Schema option to Force.
Import upgraded permission sets and permissions by using the Roles and Permissions XMLports
You import the permission sets and permissions XML files according to the following procedure.
To import the permission sets and permissions
- Delete all permission sets in the database except the SUPER permission set.
In Object Designer, run page 9802 Permission Sets, and then delete the permission sets.
- Run XMLport 9171 Import/Export Permission Sets to import the permission sets XML file,
In the request page for the XMLport, in the Direction field, choose Import, choose the OK button, and then specify the permission sets XML file.
- Run XMLport 9172 Import/Export Permissions to import the permission XML file.
In the request page for the XMLport, in the Direction field, choose Import, choose the OK button, and then specify the permissions XML file.
Set the language of the customer database
In the development environment, choose Tools, choose Language, and then select the language of the original customer database.
Add new control add-ins
The database is now fully upgraded and is ready for use. However, you may want to add the new client control add-ins that are included in Microsoft Dynamics NAV 2016. These are not added by the upgrade process. The following client control add-ins are available from the Microsoft Dynamics NAV product media:
- Microsoft.Dynamics.Nav.Client.BusinessChart
- Microsoft.Dynamics.Nav.Client.PageReady
- Microsoft.Dynamics.Nav.Client.PingPong
- Microsoft.Dynamics.Nav.Client.VideoPlayer
- Microsoft.Dynamics.Nav.Client.SocialListening
You can add control add-ins in the Control Add-ins window in the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Windows client.
I will come up with more details on this topic in my upcoming posts.






























You must be logged in to post a comment.