There is always trade-off between Quality & Quantity of deliverables.
Sometimes small Partners don’t want to invest on resources and time for their deliverables to make big profits.
Sometimes customers are not interested in paying more for their customizations requested, their after they keep investing on recursive fixes for their solutions.
Sometime requirement is not well aligned with Business Logic and the process keeps refining over the time.
Which leads to arguments on Product capability and Partner Quality of work.
Whatsoever may be the reason but before any piece of code is moved to the Production environment should be well tested and accepted by the clients/customers.
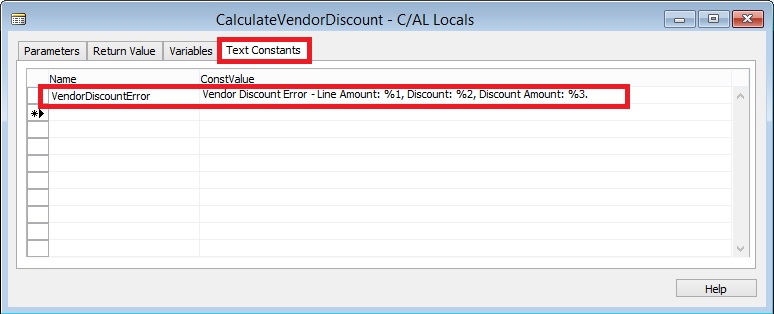
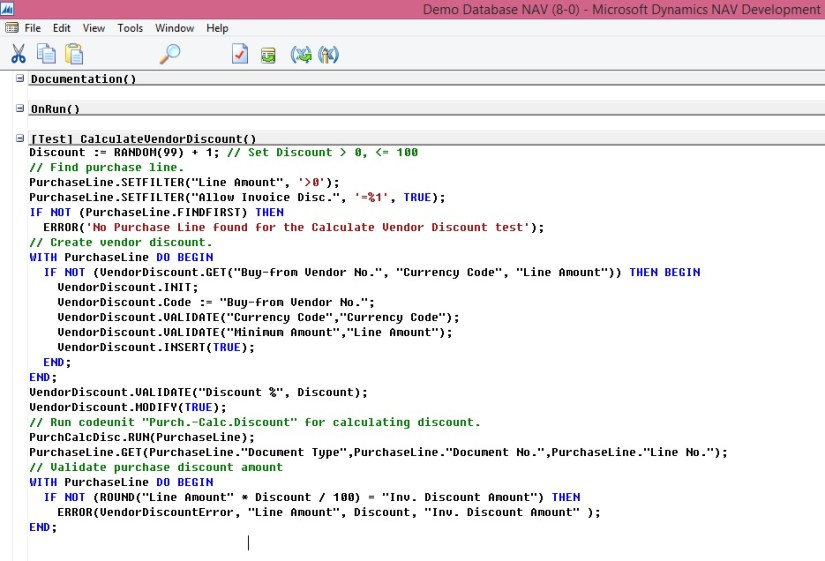
Microsoft recommends the following best practices for designing your application tests:
- Test code should be kept separate from the code that is being tested. That way, you can release the tested code to a production environment without releasing the test code.
- Test code should test that the code being tested works as intended both under successful and failing conditions. These are called positive and negative tests. The positive tests validate that the code being tested works as intended under successful conditions. The negative tests validate that the code being tested work as intended under failing conditions.
- In positive tests, the test function should validate the results of application calls, such as return values, state changes, or database transactions.
- In negative tests, the test function should validate that the intended errors occur, error messages are presented, and the data has the expected values.
- Automated tests should not require user intervention.
- Tests should leave the system in the same well-known state as when the test started so that you can re-run the test or run other tests in any order and always start from the same state.
- Test execution and reporting should be fast and able to integrate with the test management system so that the tests can be used as check-in tests or other build verification tests, which typically run on unattended servers.
- Create test functions that follow the same pattern:
- Initialize and set up the conditions for the test.
- Invoke the business logic that you want to test.
- Validate that the business logic performed as expected.
For more details see below Links:
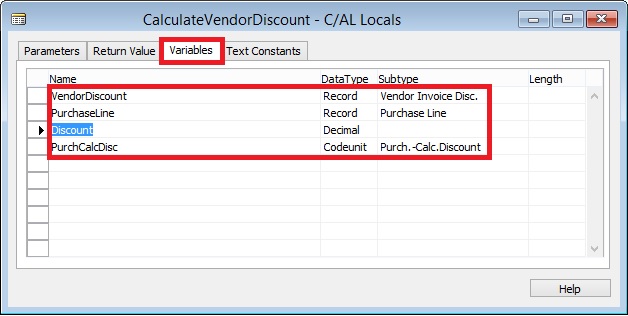
Creating a Test Codeunit and Test Function
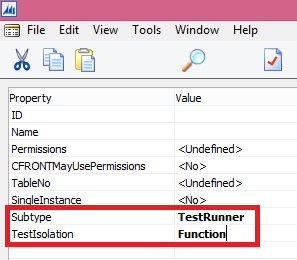
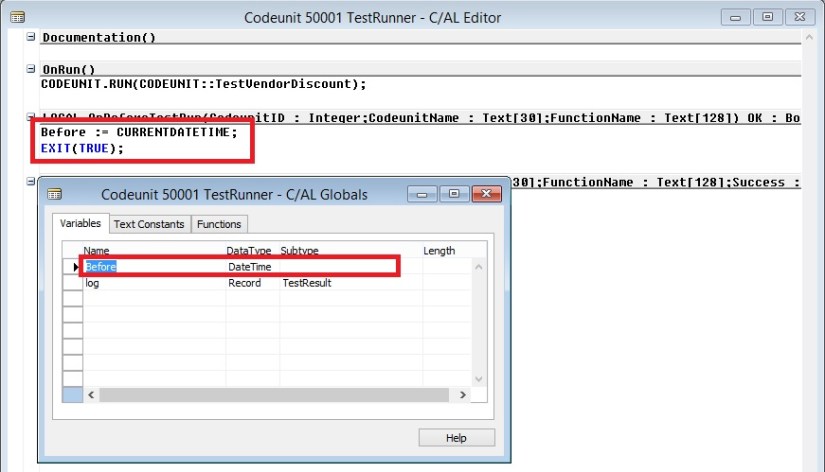
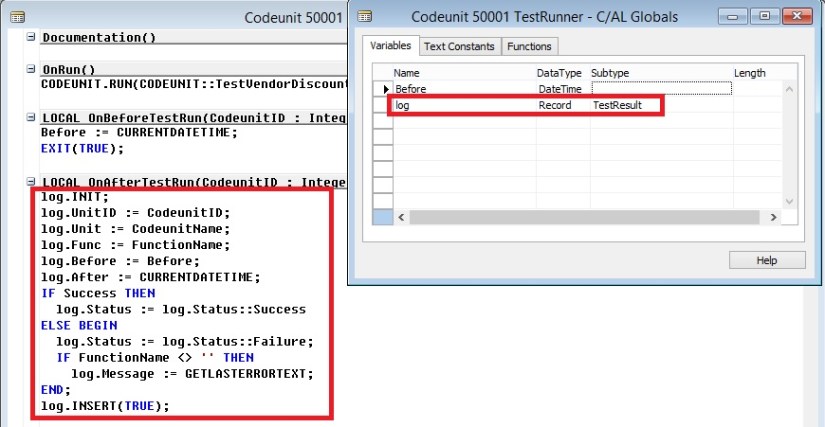
Creating a Test Runner Codeunit
Adding a Test to a Test Runner Codeunit


















You must be logged in to post a comment.