
Microsoft Dynamics NAV is Multilanguage enabled, which means that you can display the user interface (UI) in different languages.
A Multilanguage version of Microsoft Dynamics NAV is not the same as a localized version.
- A localized version is a version that is adapted to a local market. All text that is displayed to the user is translated into the local language, and all functional areas are adapted to the requirements of the local market.
- A Multilanguage version is a localized version that you can run in different languages, but all local functionality remains the same.
Language Module:
To be able to run a localized version in multiple languages, you must install language modules.
Language Module contains translated text strings of Logs & error reporting for:
- Translated strings for the UI in the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Windows client.
- Translated strings for the database.
- Translated strings for Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server, such as for logs and error reporting.
- Translated strings for the Microsoft Office Outlook Add-in for Microsoft Dynamics NAV.
- Translated strings for charts on Role Centers in the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Windows client.
- Localized versions of the client Help.
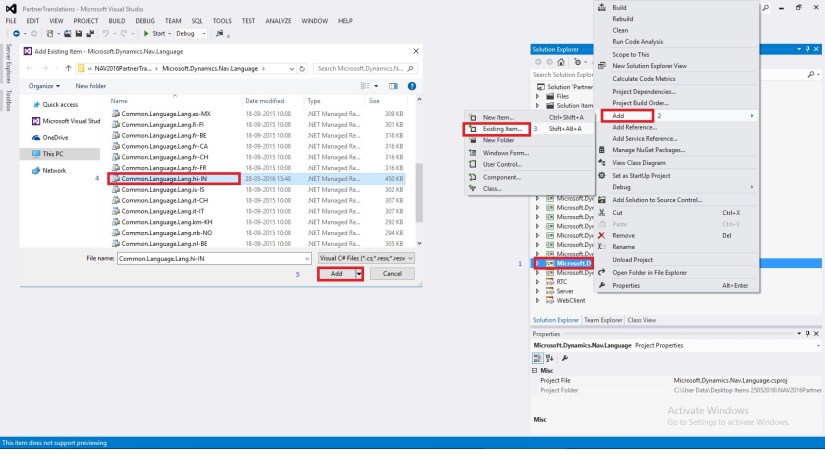
Language Modules are Binary Files which can’t be changed by any external tools for this you will require Partner Translation Tool Project and Visual Studio.
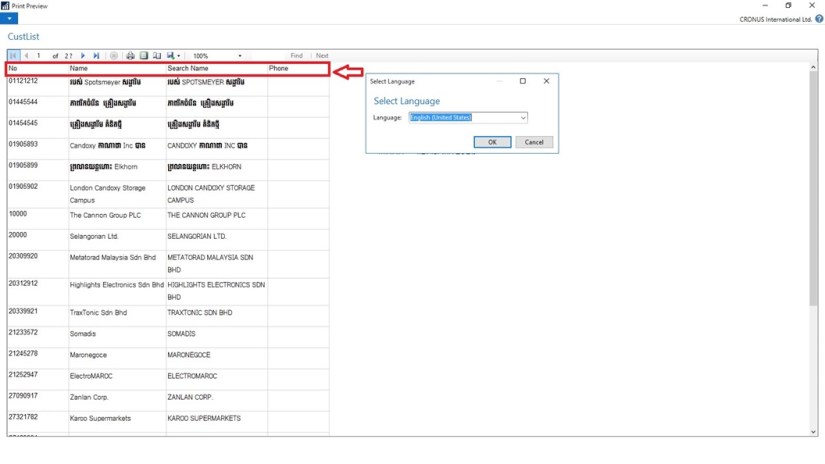
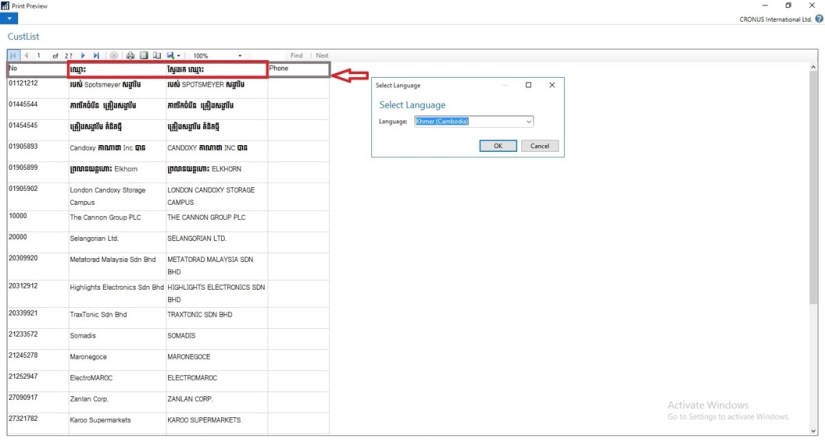
You can install language modules so that you can view text in the user interface in different languages.
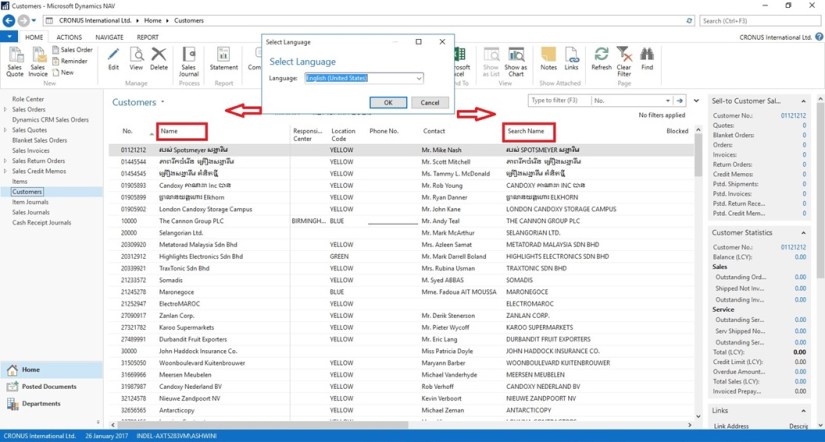
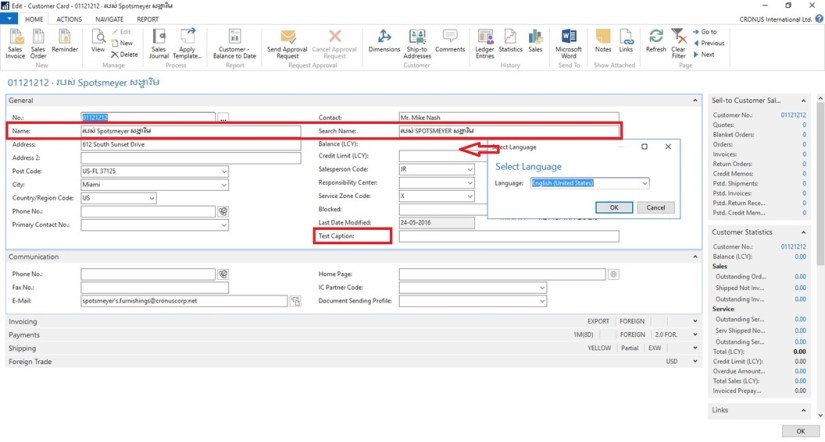
Once you have installed a language module, you can select that language on the Select Language page in the UI to change the language of all text that is displayed in the UI in captions for text boxes, on command buttons, in menus, and so on.
Imp: When you change the language of Microsoft Dynamics NAV, you are not changing the language of the data that is stored in Microsoft Dynamics NAV. Changing the text that is stored as application data is not part of the language modules.
When you install a language module, a subdirectory for the language is created in the Microsoft Dynamics NAV directory structure. The .stx, .etx, .chm, and .hh files for each language are automatically installed in the subdirectory. The name of the subdirectory is the three-letter language code (Abbreviated Name) that is used by Windows for the particular language.
You can use this link to access NAV 2016 downloads for Available – Product, Translation Tool & Language Modules. https://mbs.microsoft.com/customersource/Global/NAV/downloads/product-releases/msdnav2016download
There are 3 main parts for creating translations that works in Dynamics NAV.
- Translate the platform by translating the resource file for each DLL file.
- Translate all the captions by adding a new language into captionML in each object
- Localize development environment by translating .stx and .etx files. These 2 files have to be sent to the Microsoft regional office and sealed by Microsoft. (Only required if you want the Development Environment to be in Unsupported Language as well)
Common available resources for supported/available Language Module.
To work with Language Modules what else you required to know about: You can check below links on MSDN.
- Windows Language Virtual Table
- How to: Install Language Modules
- How to: Add Translated Strings By Importing and Exporting Multilanguage Files
- How to: Add Translated Strings By Using the Multilanguage Editor
- How to: Uninstall Language Modules
- How to: Delete Translated Strings
- Multilanguage Development
- Viewing the Application in Different Languages
Translated User Interface Strings:
In Microsoft Dynamics NAV, the user interface includes the following types of translatable user interface strings:
Captions for application objects, such as pages, tables, reports, option fields, icons, menus, and so on, that are defined in the CaptionML property for an object. Text messages that are defined in the development environment, such as text constants and error messages that are defined in the C/AL Globals window or the C/AL Locals window.
Text messages and strings that are defined in Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server and Microsoft Dynamics NAV Windows client.
To add a language to the text messages that are defined in the resource files for Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server and Microsoft Dynamics NAV Windows client, special tools are required.
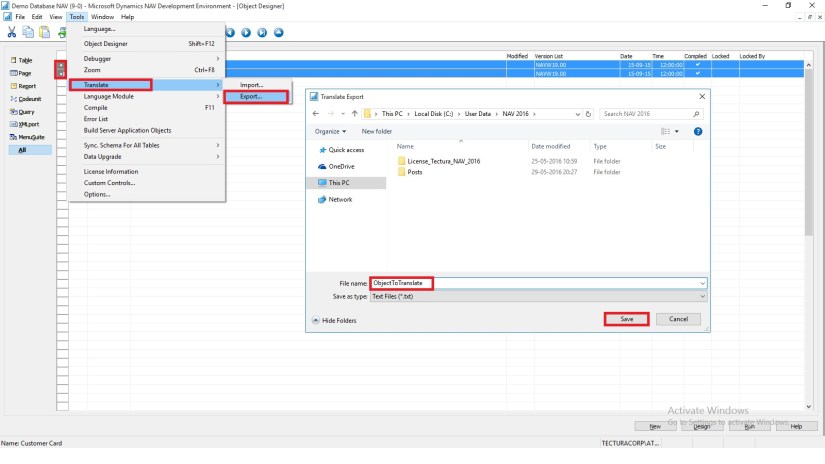
You can manage translations by using text files. In the development environment, you can export all strings for the specified objects to a text file, translate the strings in a translation tool of your choice, and then import the new translations. Then, when you compile the updated objects, the new translations are available to users in the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Windows client.
Multilanguage across Conflicting Text Encoding Formats:
To support users with translated strings across conflicting text encoding formats, you must save the translations to a text file in UTF-8 text encoding format.
This converts the file to Unicode, which Microsoft Dynamics NAV Development Environment cannot import. Instead, you add the files to a dedicated Translations folder on the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server computer.
The default location of this folder is:
C:\Program Files\Microsoft Dynamics NAV\90\Service\Translations.
When you have more than one service instance, there is a Translations folder for each service instance, such as:
C:\Program Files\Microsoft Dynamics NAV\90\Service\Instances\MyInstance\Translations.
Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server adds any strings in text files that you place in the relevant Translations folder to the metadata for Microsoft Dynamics NAV.
To add translated strings for a conflicting text encoding format:
In the development environment, export the strings for the objects that you want to translate.
Translate the strings in the resulting text file into desired Language by using your preferred translation process.
When translations are complete, save the translated strings into a text file in the UTF-8 text encoding format. The extension of the file must be .txt.
It is recommend that you remove the other Language strings from the Unicode file before you copy it to the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server computer.
Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server queries the Translations folder for updated strings, and for performance reasons the folder should only contain strings that you cannot import into the development environment because of conflicting codepages.
Copy the UTF-8 file to the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server computer.
C:\Program Files\Microsoft Dynamics NAV\90\Service\Translations
When you have more than one service instance, there is a Translations folder for each service instance, such as:
C:\Program Files\Microsoft Dynamics NAV\90\Service\Instances\MyInstance\Translations.
Restart the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server instance.
Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server adds the translated strings in the file to the metadata store for the Microsoft Dynamics NAV deployment.
Now Users of this Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server session can now change the user interface language from English to required Language.
The metadata store is updated whenever you add new strings to the Translations folder and then restart the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server service instance. Cached strings are not deleted from the metadata store when you restart the service instance.
I will comeup with more details in my upcomming post soon.
























You must be logged in to post a comment.