Upgrade Considerations Preparing for Upgrade in Microsoft Dynamics NAV 2016
If your solution includes variables where the name is now used by a standard C/AL function or statement such as REGISTERTABLECONNECTION or FOREACH, you must change the variables before you upgrade to Microsoft Dynamics NAV 2016. Alternatively, you can enclose the variable names in quotation marks.
If you are upgrading a solution that depends on functionality that is deprecated or changed in the default version of Microsoft Dynamics NAV 2016, you must verify that the upgrade codeunits migrate data correctly. From 2013-R2 not yet reported any under this category.
When you introduce changes to the database schema in Microsoft Dynamics NAV 2016, Microsoft Dynamics NAV will check if these changes are destructive or not. If the database check indicates that the change may lead to data deletion, such as if you are dropping a table column so that the contents of that column will be deleted, this is considered a destructive change. You will be prompted to handle the situation using upgrade codeunits. You can check out my earlier post on this topic here. Data Upgrade – in Navision 2015 it still valid for 2016, I will come up with any specific differences in my upcoming post later.
If a company name includes a special character, an error may display during the upgrade. In this context, special characters include the: [ ~ @ # $ % & * ( ) . ! % – + / = ? ]. If you are going to upgrade a database where one or more company name includes a special character, it is recommend that you rename the company before you start the upgrade process. After the upgrade is successfully finished, you can rename the company again.
Versions later than Microsoft Dynamics NAV 2013 R2 require that all columns in all system tables are in English. As a result, if you try to open a database with non-English system tables in Microsoft Dynamics NAV 2013 R2 or later, an error displays, saying that one or more columns do not exist. Make sure that all objects where compiled in a development environment with the right .ETX and .STX files. You can verify that you are running in the correct environment with English (US) as the base language by opening the ndo$dbproperty table in SQL Server Management Studio. In the Identifiers column, the word Object must be written exactly as shown here.
Converting a Database in Microsoft Dynamics NAV 2016
Before you start, make sure that you have applied the changes that are described in KB 2804640
Code corrections for some Microsoft Dynamics NAV 2013 reports to prevent compilation errors with Report Viewer 2012 when upgrading to later versions of Microsoft Dynamics NAV. Your will require to use partner login to access the hotfix. Click here for the Link.
You can choose to convert the old database and not upgrade your application. However, it is recommend that you upgrade the application objects as well so that your solution includes important application fixes and new functionality that is introduced in Microsoft Dynamics NAV 2016.
Upgrading the application will also reduce the amount of merging required to upgrade to the next major version of Microsoft Dynamics NAV, bringing you to the latest version of the product faster.
Preparing the Old Database for Conversion
- Make a copy of the old database or create full database backup.
I have copied the database (Navision 2013/R2) and attached to the SQL for this operation:

- Clear all Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server instance records from the dbo.Server Instance table in the database on SQL Server.

You can do this by using SQL Server Management Studio to open and clear the table.
- Open the development environment that matches the Microsoft Dynamics NAV version of the old database, and then connect to the old database.
- In Object Designer, make sure that no objects are locked.
If any objects are locked, the conversion process will not update the database version number. As a result, the conversion will not complete.
- On the Tools menu, choose Build Server Application Objects, and then choose the Yes button.
- If any errors occur, they are shown in the Error List window. Make sure that you address all compilation errors before you continue.
- Upload the Microsoft Dynamics NAV 2016 Partner license to the database
The license that you upload must be a developer license. During the conversion, the development environment will convert the report objects that are stored in the old database to the RDL 2012 format.
- If you are converting a Microsoft Dynamics NAV 2013 R2 or Microsoft Dynamics NAV 2015 database, then run the Sync-NavTenant cmdlet from the Microsoft Dynamics NAV 2013 R2 or Microsoft Dynamics NAV 2015 Administration Shell to synchronize the database schema changes.
Converting the Old Database
Next, we will convert the old database so that it can be used in Microsoft Dynamics NAV 2016.
Before you start the following procedure, you can choose to uninstall Microsoft Dynamics NAV 2013, Microsoft Dynamics NAV 2013 R2, or Microsoft Dynamics NAV 2015. When you uninstall Microsoft Dynamics NAV 2013, Microsoft Dynamics NAV 2013 R2, or Microsoft Dynamics NAV 2015, the database is still attached to the instance of SQL Server, which you can verify using SQL Server Management Studio.
To convert the database
- Install Microsoft Dynamics NAV 2016.
- Open the Microsoft Dynamics NAV 2016 development environment, and then connect to the database that you prepared in the previous task.
- In the dialog box that appears, read the instructions carefully because this action cannot be reversed. When you are ready, choose the OK button, and then choose the OK button to confirm that you want to convert the database.
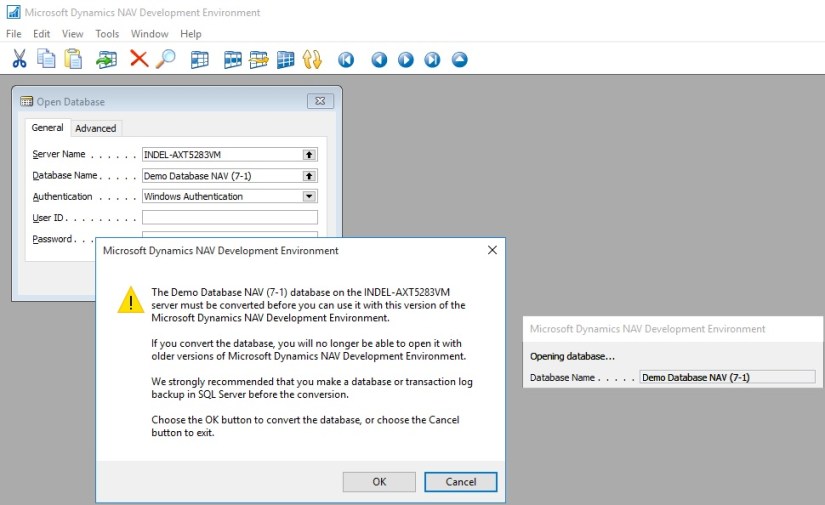
Microsoft Dynamics NAV will now convert the database. This includes an upgrade of system tables, and an upgrade of all reports to support Report Viewer 2012.
- When you are notified that the conversion was successful, choose the OK button.


- Connect a Microsoft Dynamics NAV 2016 Server instance to the converted database.
You use the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server Administration tool to connect a Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server instance to the converted database.

In addition, you must add the service account that is used by the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server instance as a member of the db_owner role in the Microsoft Dynamics NAV database on SQL Server.
It is also possible to script these steps in SQL Server Management Studio:
USE [master]
GO
CREATE LOGIN [domain\accountname] FROM WINDOWS
CREATE USER [domain\accountname] FOR LOGIN [domain\accountname]
GRANT SELECT ON [master].[dbo].[$ndo$srvproperty] TO [domain\accountname]
GO
USE [Microsoft Dynamics NAV Database]
GO
CREATE USER [domain\accountname] FOR LOGIN [domain\accountname]
ALTER ROLE [db_owner] ADD MEMBER [domain\accountname]
GRANT VIEW DATABASE STATE TO [domain\accountname]
You can check more details from my earlier post Provisioning the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server Account.
- Run the development environment as an administrator, and then set the development environment to use the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server instance that connects to the database.
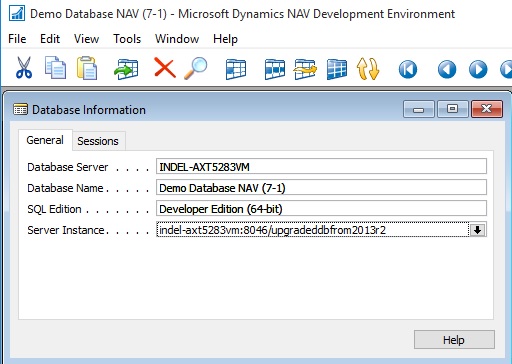
- Run the schema synchronization to complete the database conversion.
You can run the schema synchronization from the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Development Environment or Microsoft Dynamics NAV 2016 Administration Shell.

From the development environment:
Open development environment as an administrator. On the Tools menu, choose Sync. Schema For All Tables, and then choose With Validation and follow the schema synchronization instructions.
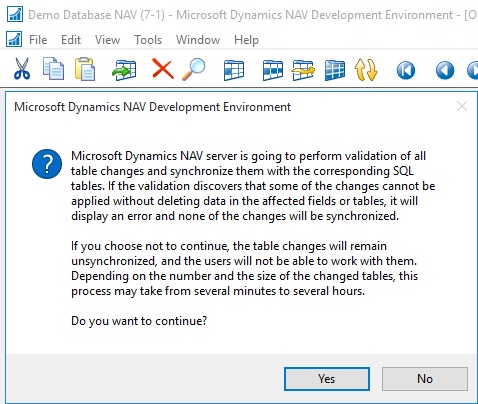

From the Microsoft Dynamics NAV 2016 Administration Shell:
Open the Microsoft Dynamics NAV 2016 Administration Shell as an administrator, and then run Sync-NavTenant cmdlet as follows:
Sync-NavTenant –ServerInstance <ServerInstanceName>
Replace <ServerInstanceName> with the name of the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server instance that is connected to the database
- If the database references any assemblies (such as client control add-ins) that are not included on the Microsoft Dynamics NAV 2016 installation media (DVD), then add the assemblies to the Add-ins folder on Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server or Microsoft Dynamics NAV Windows client computers.
For the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Windows client, the default path is C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Dynamics NAV\90\RoleTailored Client\Add-ins folder.
For Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server, the default path is the C:\Program Files\Microsoft Dynamics NAV\90\Service\Add-ins folder
In the development environment, on the Tools menu, choose Build Server Application Objects, and then, in the dialog box, choose the Yes button.

- Fix compilation errors.
You can find all objects which did not compile in the Object Designer window, by setting a field filter on the Compiled field.
- Upload the customer license to the converted database.
You have now completed the conversion of the Microsoft Dynamics NAV 2013, Microsoft Dynamics NAV 2013 R2, or Microsoft Dynamics NAV 2015 database to be accessed from Microsoft Dynamics NAV 2016. To test the converted database, you can connect it to the Microsoft Dynamics NAV 2016 Server instance that by Microsoft Dynamics NAV clients, and then open a client.
You may encounter some login issues to resolve it here are the few tips:
Delete the user login details as we do in earlier versions when RTC was introduced to access any database using SQL Query as below :
USE [Demo Database NAV (7-1)] (use your database name)
GOdelete from [dbo].[User]
delete from [dbo].[Access Control]
delete from [dbo].[User Property]
delete from [dbo].[Page Data Personalization]
delete from [dbo].[User Default Style Sheet]
delete from [dbo].[User Metadata]
delete from [dbo].[User Personalization]
After this if you get error stating you don’t have permission to codeunit ApplicationManagement give permission in SQL to the Login running the service as below:

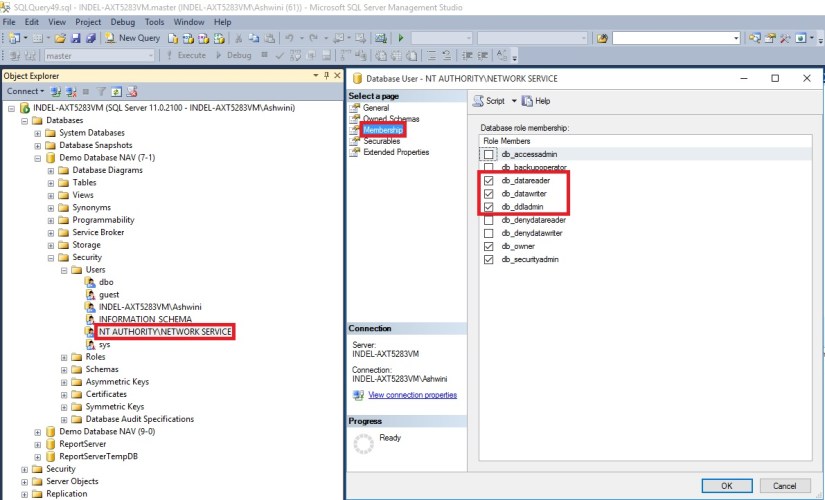
Next, upgrade the application code to Microsoft Dynamics NAV 2016.
I will come up with more details in my upcoming posts.

















You must be logged in to post a comment.