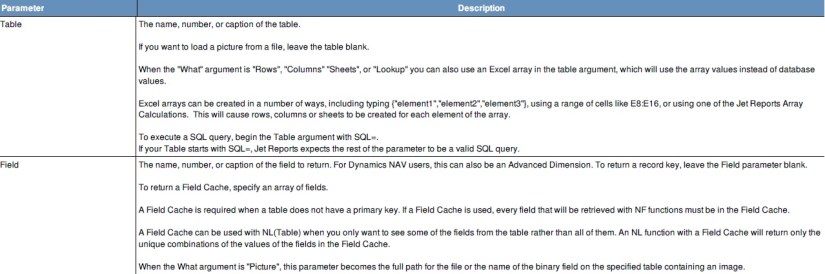
LINK gives users advanced filtering capabilities in Jet Essentials.
Using LINK allows users to tie together information from different tables.
LINK is available for all connector types.
Recall from my previous post where I introduced with NL Function, you can find the Link here.
Since Link is used in Combination with NL Function so recalling it is necessary here, if you have not seen the previous post please follow the link above to understand the functionality, before you continue.
Let’s start with simple NL Function usage, later we will see its usage with Link.
The following formula will return the document number for each Sales Invoice Header in the system.
=NL(“Rows”,”Sales Invoice Header”,”No.”)
The following formula will return only sales invoices where the posting date is within a specific data range.
=NL(“Rows”,”Sales Invoice Header”,”No.”,”Posting Date”,”>1/1/2009″
LINK can be used to filter on a field that is not in the Sales Invoice Header table (such as the “Type” field in the Sales Invoice Line table) as follows:
=NL(“Rows”,”Sales Invoice Header”,”No.”,”Posting Date”,”>1/1/2009″,”LINK=”,”Sales Invoice Line”,”Document No.”,”=No.”,”Type”,”Item”)
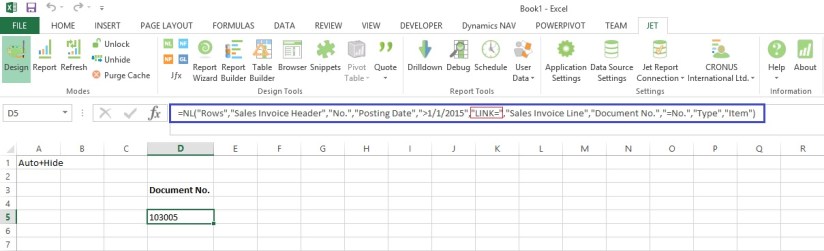
In this example, we used LINK= and specified the Sales Invoice Line table because this is where the “Type” field that we want to filter exists. We linked to the Sales Invoice Header by specifying that the “Document No.” Field on the Sales Invoice Line matches the “No.” field on the Sales Invoice Header.
We then specified the “Type” filter on the Sales Invoice Line table.
Please note that some relationships between tables may require more than a single field to define the link:
=NL(“Rows”,”Purch. Rcpt. Line”,,”Link=”,”Purch. Inv. Line”,”Document No.”,”=Order No.”,”Line No.”,”=Order Line No.”,”Posting Date”,”>1/1/2010″)
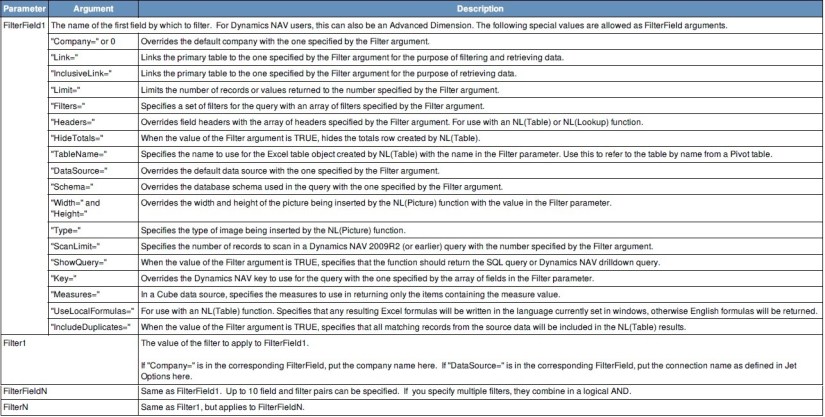
Nested Linking
LINK statements can be combined to fulfil more complex filtering requirements.
For example, assume that you would like to see the territories with sales during a given period.
A simple formula could be used if the territory is available on the table that contains the historical sales information and if you wanted the territory assignment at the time that the sale was made.
If, on the other hand, the territory is not available, or you want the currently assigned territory, you can do this by combining LINK statements as follows:
=NL(“rows”,”Country/Region”,”Code”,”Link=”,”Customer”,”country/Region Code”,”= Code”,”Link=”,”Sales Invoice Header”,”Sell-to Customer No.”,”=No.”,”Posting Date”,”>1/1/2010″)
In this example we linked the Country/Region to the Customer and the Customer to the Sales Invoice Header. Then we filtered by the “Posting Date” field to get Country/Region with sales for a specific period.
Linking Multiple Tables
LINK statements can also be combined to handle situations where a single table is linked to multiple tables.
For example, want to see Sales Invoices where the Country/Region Code is “AE” and the Vendor is “30000”.
To do this we can link from the Sales Invoice Line table to the Customer table with the “field filtered for “AE” and, in addition, link from the Sales Invoice Line table to the Item table with the “Vendor No. filtered for “30000”.
=NL(“Rows”,”Sales Invoice Line”,,”Type”,”Item”,”Link=”,”Customer”,”No.”,”=Sell-to Customer No.”,”Country/Region Code”,”=AE”,”Link=”,”Item”,”No.”,”=No.”,”Vendor No.”,30000)
Note that the Link statements include the primary table (Sales Invoice Line) which indicates that links should restart from the primary table rather than linking in the nested fashion demonstrated in the previous section. It is possible to mix these models and have multiple links as well as nested links.
One other thing to note is that filters applied to the primary table (like the filter on the “Type” field in this example) should occur before any LINK statements.
NL(“Link”)
The NL(Link) function can be used to specify linked tables when more than 10 parameters are needed for a linking statement.
This example formula was used in the nested link section and links from the Country/Region table to the Customer table and then from Customer table to the Sales Invoice Header table.
=NL(“Rows”,”Country/Region”,”Code”,”Link=”,”Customer”,”Country Region Code”,”=Code”,“Link=”,”Sales Invoice Header”,”Sell-to Customer No.”,”=No.”,”Posting Date”,”>1/1/2009”)
Enter in Excel Sheet Below Formula:
[Cell E4] =NL(“Rows”,”Country/Region”,”Code”,”Link=”,F4)
[Cell F4] =NL(“Link”,”Customer”,,”Country/Region Code”,”=Code”,”Link=”,G4)
[Cell G4] =NL(“Link”,”Sales Invoice Header”,,”Sell-to Customer No.”,”=No.”,”Posting Date”,”>1/1/2010″)
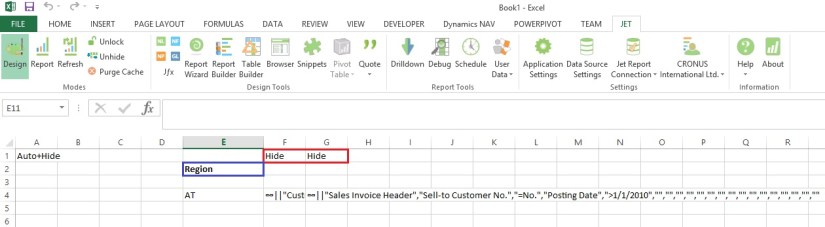
Explanation as below:

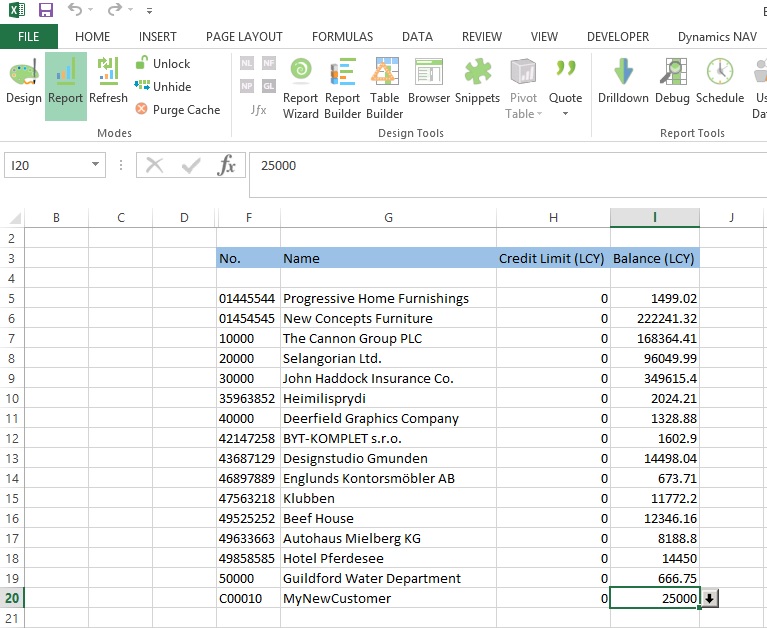
When we execute the Report Output will be as below:

Stay tuned for more details in my Upcoming posts.
28.620561
77.437322



































You must be logged in to post a comment.